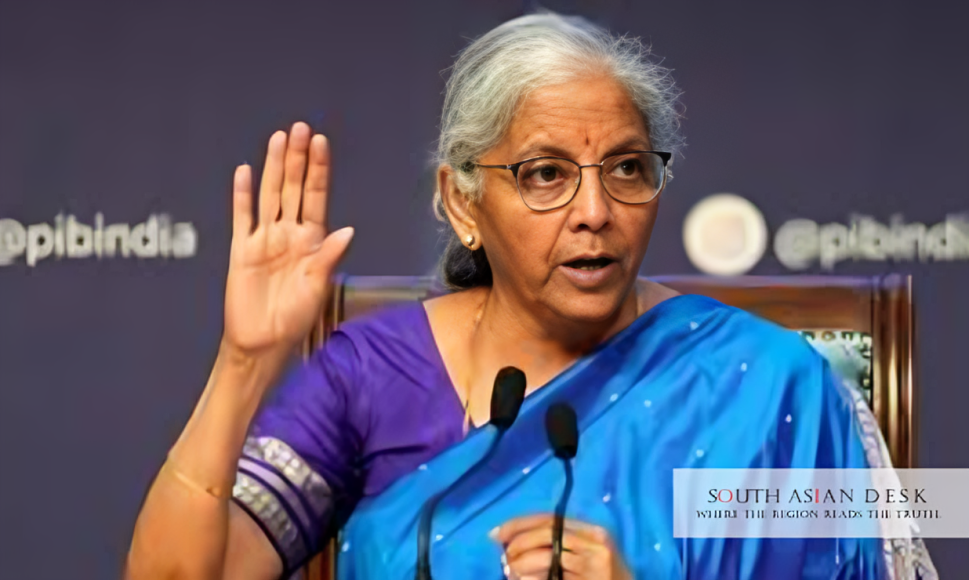
India’s Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced on Friday, October 3, 2025, in New Delhi, that the government will elevate capital spending to a record ₹11.21 trillion for the fiscal year ending March 2026. This move anchors India growth resilience in domestic drivers, shielding the economy from global disruptions like US tariffs. The decision responds to robust first-quarter expansion and aims to sustain momentum into 2025.
This commitment holds significance for South Asia, where India’s accelerated development bolsters regional supply chains, boosts cross-border investments, and fosters economic interdependence. As the subcontinent’s largest economy, India’s steady ascent influences trade volumes with neighbours such as Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka, potentially easing inflationary pressures and enhancing connectivity via initiatives like the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor.
Nirmala Sitharaman India Growth No Complacency 2025
Nirmala Sitharaman India growth no complacency 2025 emerged as a core theme in her recent remarks. She emphasised that India’s expansion relies on stable consumption and investment shares in GDP. “With the steady share of consumption and investment in the overall GDP over the years, India’s growth is firmly anchored in its domestic factors, which minimises the impact of external shocks on overall growth,” Sitharaman stated.
She urged a mindset of “quiet confidence” in policy execution, warning against overconfidence. This stance aligns with the Economic Survey 2024-25, tabled in January 2025, which projects real GDP growth at 6.4 per cent for FY25 and 6.3 to 6.8 per cent for FY26. The survey highlights domestic steadiness amid global uncertainties, crediting fiscal discipline and a services trade surplus for buffering volatility.
Recent data underscores this resilience. The economy grew 7.8 per cent year-on-year in the April-June quarter of 2025, marking the fastest pace in five quarters and surpassing the prior 7.4 per cent. Rural demand recovery and easing food inflation further support the outlook. The Reserve Bank of India maintained its policy rate at 5.5 per cent this week, hinting at possible December cuts to counter tariff effects and recent consumption tax reductions.
Sitharaman’s call for Nirmala Sitharaman India growth no complacency 2025 resonates in policy circles. It reflects lessons from past reforms that have elevated India to the world’s fastest-growing major economy. Over the last decade, structural changes have drawn global capital, with foreign exchange reserves hitting record highs. Yet, the minister stressed proactive measures to navigate headwinds like geopolitical tensions and supply chain shifts.
Capital Expenditure Surge Powers India Growth Resilience
The cornerstone of this strategy is a sharp rise in capital expenditure, or capex, to ₹11.21 trillion for FY26, equivalent to 3.1 per cent of GDP. This marks an increase from the revised estimate of ₹10.18 trillion for FY25. Total expenditure for FY26 stands at ₹50.65 trillion, with receipts excluding borrowings at ₹34.96 trillion.
This allocation prioritises infrastructure, a key pillar of India growth resilience. Funds will flow into roads, railways, and urban development, aiming to create jobs and enhance productivity. The Budget 2025-26 earmarks ₹1.5 trillion for 50-year interest-free loans to states, tied to reform incentives. This decentralised approach ensures balanced regional growth, vital for South Asia’s interconnected markets.
Key Infrastructure Allocations
Several targeted outlays amplify the impact:
- Asset Monetisation Plan 2025-30: Targets ₹10 trillion to reinvest in fresh projects, unlocking value from existing assets like airports and highways.
- Nuclear Energy Mission: ₹20,000 crore for small modular reactors, with five indigenous units planned by 2033, bolstering energy security.
- Maritime Development Fund: Corpus of ₹25,000 crore, with up to 49 per cent government contribution, to modernise ports and spur exports.
- SWAMIH Fund 2: ₹15,000 crore to complete 100,000 affordable housing units, addressing urban housing shortages.
These initiatives build on FY25’s momentum, where capex supported a 6.2 per cent industrial sector expansion. Services exports grew 12.8 per cent in April-November 2025, outpacing the 11 per cent trend from FY14-23. Agriculture rebounded with 3.5 per cent growth in Q2 FY25, aided by record kharif foodgrain output of 1,647.05 lakh metric tonnes.
Nirmala Sitharaman India growth no complacency 2025 guides these efforts. The government views investment as the third engine of development, alongside agriculture, MSMEs, and exports. Enhanced MSME limits, turnover up 2.5 times, investment doubled will channel ₹10,000 crore via a new Fund of Funds. An Export Promotion Mission, integrated with ‘BharatTradeNet’, targets documentation and financing hurdles.
Background: From Budget to Execution
The Union Budget 2025-26, presented by Sitharaman on February 1, 2025, laid the groundwork for this capex escalation. It projected FY25 growth at 6.4 per cent, with FY26 estimates reflecting cautious optimism. Revised FY25 figures adjusted total expenditure to ₹47.16 trillion, underscoring adaptive fiscal management.
India’s track record bolsters confidence. Over the past 10 years, capex has tripled, driving rapid infrastructure progress. The economy surpassed pre-pandemic gross value added levels in H1 FY25, with inflation contained below 5 per cent. Forex reserves and remittances provide additional buffers, minimising external vulnerabilities.
This evolution ties into broader South Asian dynamics. India’s growth spills over via trade pacts like SAFTA and BIMSTEC, where enhanced ports and digital corridors facilitate intra-regional flows. Neighbouring economies benefit from Indian FDI, with Bangladesh and Nepal seeing upticks in manufacturing tie-ups.
What’s Next for India Growth Resilience
Looking ahead, execution remains key to Nirmala Sitharaman India growth no complacency 2025. The government eyes public-private partnerships for a three-year infrastructure pipeline, including ₹1 trillion Urban Challenge Fund for smart cities. Potential RBI rate easing could stimulate private investment, while monitoring US tariff impacts.
Monitoring global cues, such as IMF’s 6.5 per cent medium-term forecast, will shape adjustments. Digital economy targets surpassing $1 trillion by 2025 promise further resilience through e-commerce and data centres.
In conclusion, this capex infusion cements India growth resilience as a strategic imperative. By prioritising domestic anchors and vigilant policymaking, India charts a resilient path through 2025’s uncertainties, inspiring regional stability.
Published in SouthAsianDesk, October 3rd, 2025
Follow SouthAsianDesk on X, Instagram, and Facebook for insights on business and current affairs from across South Asia.